# 类组件
# state 和 setState
- setState(updater,[callback])
- updater: 更新数据 function/object
- callback: 更新成功后的回调 function
- 异步:react 通常会集齐一批需要更新的组件,然后一次性更新来保证渲染的性能
- 浅合并 Object .assign()
- 调用 setState 之后,会触发生命周期,重新渲染组件
import { react, Component } from "react";
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "yunfei",
};
}
handler() {
this.setState({ name: "wang" });
this.setState(() => {
return { name: "wang" };
});
this.setState({ name: "wang" }, () => {
console.log("callback");
});
}
render() {
const { name } = this.state;
return (
<div>
{name}
<button onClick={() => this.handler}> setName </button>
</div>
);
}
}
批处理 正常情况下,在一个操作中多次调用 setState,React 会合并这些更新,只更新一次组件 setState 是同步也是异步的
在 React 中 state 是不可变值,修改 state 的唯一办法是,调用 setState 根据原有 state 映射出一个新的 state
- setState 在批更新机制下,表现为异步,否则为同步
- setState 在 React 可以控制的方法中(React 的生命周期函数 & React 事件) 表现为异步,在微任务中以及 DOM 事件中,表现为同步
class App extends Component {
state = {
count: 1,
};
addCount = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
});
console.log(this.state.count); //
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
});
console.log(this.state.count); //
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
});
console.log(this.state.count); //
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
});
console.log(this.state.count); //
};
render() {
console.log("render");
const { count } = this.state;
return (
<div>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={this.addCount}>递增1</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.addCount();
});
}}
>
递增2
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
递增 1
1 1 1 1 render
递增 2
render 2 render 3 render 4 render 5
# 组件间通信
React.js 中 数据是从上自下流动(传递)的,也就是一个父组件可以把他的 state/props 通过 props 传递给他的子组件,但是子组件不能修改 props - React.js 是单向数据流。如果子组件需要修改父组件状态(数据),是通过回调函数方式来完成
父 向 子 通信 把数据添加子组件的属性中,然后子组件中重 props 属性中,获取父级传递过来的数据
子 向 父 通信
在父级中定义相关的数据操作方法(或其他回调),吧该方法传递给子级,在子级中调用该法父级传递消息
import React, { Component } from "react";
class App extends Component {
state = {
name: "yunfi",
age: 18,
};
setName = (name) => {
this.setState({ name });
};
render() {
const { age } = this.state;
return (
<div>
<h3>{name}</h3>
<Foo age={age} setName={this.setName} />
</div>
);
}
}
class Foo extends Component {
render() {
const { setName, age } = this.props;
return (
<div>
<div>age:{age}</div>
<button onClick={setName("wang")}>set-name</button>
</div>
);
}
}
# 跨组件通信 context - 扩展
React.createContext(defaultValue); {Consumer,Provider} = createContext(defaultValue);
context.Provider 在父组件嗲用 Provider 传递数据 -value 要传递的数据
接受数据
class.contextType = Context;
static contextType = Context;
- this.context;
Context.Consumer
使用 ```jsx <Consumer> {(props) => { console.log(props); return <div></div>; }} </Consumer> ```注意在使用不熟练时,最好不要在项目中使用 context,context 一般给第三方库使用
实例
context.js 创建上下文对象
import { createContext } from "react";
const context = createContext();
const { Provider, Consumer } = context;
export { Provider, Consumer };
export default context;
App.js 封装、初始化数据
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { Provider } from "./context.js"; //引入上下文
import Child from "./child.js"; //子组件
class App extends Component {
state = {
name: "yunfei",
age: 18,
count:0
};
// 新增
addCount = ()=>{
this.setState({count,this.state.conut++});
}
render() {
const { name, age } = this.state;
return (
// Provider 的 value 属性中定义的是要传递给后代组件的数据
<Provider value={name, age,addCount:this.addCount}>
<Child />
</Provider>
);
}
}
child.js 使用数据
import React, { Component } from "react";
import context from "./context.js"; // 引入上下文对象
class Child extends Component {
static ContextType = context; // 赋值
render() {
const { name, age, count, addCount } = this.context; // 结构上下文对象数据
return (
<div>
<p>name:{name}</p>
<p>age:{age}</p>
<p>count: {count}</p>
<button onClick={addCount}> 新增 </button>
</div>
);
}
}
ChildConsumer.js
import { Component } from "react";
import { Consumer } from "./context.js";
class ChildConsumer extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Consumer>
{({ name }) => {
// 解构
return <div>name:{name}</div>;
}}
</Consumer>
);
}
}
# 受控组件
当想要获取表单的一些内部状态时,就可以将表单的内部状态和组件的状态进行绑定,这样就形成受控组件 受控组件: 让 表单控件 的内部状态 和我们 state 保持一致
非受控组件: 我们不需要同步 value 值(defaultValue,defaultChecked)
import React, { Component } from "react";
class App extends Component {
state = {
name: "yunfei",
};
change(e) {
this.setState({ name: e.target.value });
}
render() {
const { name } = this.state;
return (
<div>
受控组件
<input type="text" value={name} onChange={(e) => this.change(e)} />
非受控组件
<input type="text" defaultValue={name} />
</div>
);
}
}
# 组件的生命周期
生命周期 是指 某个事物从开始到结束的各个阶段,当然在 React.js 中值的是组件从创建到销毁的过程,React.js 在这个过程中的不同阶段调用的函数,通过这些函数,可景区的对组件进行控制
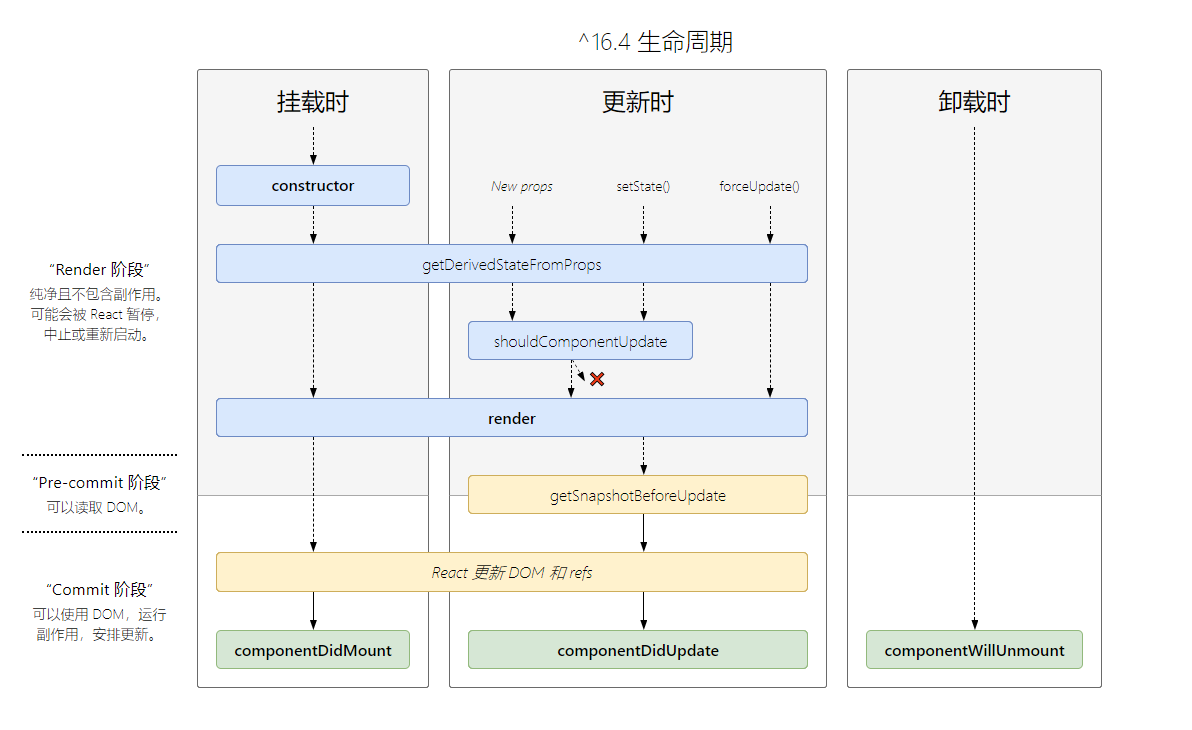
# 生命周期延边
生命周期 16.3 之前 16.3 16.4 及 之后
挂载阶段(组件创建-->把组 件创建的
虚拟DOM,生成真实DOM,添加到我们的 DOM 树中)- constructor
- static get DerivedStateFromProps(props) 将 props 中的内容关联到 state 中
- 注意 this 问题
- render
- componentDidMount -- 组件完成挂载 处理副作用(请求)
更新阶段 -- 组件重新渲染 组件更新:
- 调用 setState 会进行组件更新
- 在 React 父组件更新会引起子组件进行更新
- static getDerivedStateFromProps(props,state)
- shouldComponentUpdate() -- 判断是否更新
- render()
- getSnapshotBeforUpdate();
- componentDidUpdate() -- 处理副作用(请求)
卸载阶段
- componentWillUnmount -- 删除添加在全局的一些信息或操作
